Gout
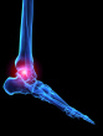
What is gout?
Gout is a type of arthritis that is caused by having too much uric acid in the joints. Uric acid is a substance that forms when your body breaks down a substance called purines. Uric acid usually dissolves in your blood and passes through your kidneys into your urine. In people with gout, uric acid builds up and forms sharp crystals that can collect around the joints. This causes pain and swelling in the affected joints.
Symptoms
The pain can be very intense and can occur suddenly for no apparent reason. It often affects the big toe joint and it usually occurs at night. The affected joint becomes red, feels hot and hurts a lot. It will be more painful if you touch it. Other parts of the body where gout attacks occur include the top of the foot and the ankle joint. Gout can affect other joints in your body but it is most prevalent in the foot.
Who can get gout?
Gout is most common in people who are overweight, drink alcohol or have high cholesterol. Men have gout more often than women do, although women are more likely to have gout after menopause. In addition, some people who eat foods that contain a lot of purines are prone to gout attacks. Some of these foods that are high in purines include:
Some medicines are also believed to make gout more likely. These include:
• certain diuretics (“water pills”)
• niacin (a B-complex vitamin)
• aspirin (taken in low doses)
• cyclosporine (brand names: Sandimmune, Neoral, SangCya)
• some drugs used to treat cancer
Treatment
Treatment is generally performed by your GP via medications and diet control. If you don’t get treatment, a gout attack can last for days or even weeks. If you keep having more attacks, more joints will be affected, and the attacks will last longer.
If you have gout attacks for many years, you may develop soft tissue swellings of uric acid crystals called tophi in your joints. Tophi usually form on the toes, fingers, hands and elbows. You may also get kidney disease or kidney stones. Over time, the bone around a joint may be destroyed by gout causing arthritis in that joint.
To help prevent gout, your doctor may prescribe medicines to prevent future gout attacks. These medicines can help wash the uric acid from your joints, reduce swelling and keep uric acid from forming.
If you are overweight, it is helpful to lose the weight, even half a kilogram will help your joints. If you have high blood pressure or high cholesterol, get treatment and follow a low-salt, low-fat diet. Stay away from alcohol and foods that are high in purines and drink plenty of water to help flush the uric acid from your body.
Gout is a type of arthritis that is caused by having too much uric acid in the joints. Uric acid is a substance that forms when your body breaks down a substance called purines. Uric acid usually dissolves in your blood and passes through your kidneys into your urine. In people with gout, uric acid builds up and forms sharp crystals that can collect around the joints. This causes pain and swelling in the affected joints.
Symptoms
The pain can be very intense and can occur suddenly for no apparent reason. It often affects the big toe joint and it usually occurs at night. The affected joint becomes red, feels hot and hurts a lot. It will be more painful if you touch it. Other parts of the body where gout attacks occur include the top of the foot and the ankle joint. Gout can affect other joints in your body but it is most prevalent in the foot.
Who can get gout?
Gout is most common in people who are overweight, drink alcohol or have high cholesterol. Men have gout more often than women do, although women are more likely to have gout after menopause. In addition, some people who eat foods that contain a lot of purines are prone to gout attacks. Some of these foods that are high in purines include:
- Beer, other alcoholic beverages.
- Anchovies, sardines in oil, fish roes, herring.
- Yeast.
- Organ meat (liver, kidneys, sweetbreads)
- Legumes (dried beans, peas)
- Meat extracts, consomme, gravies.
- Mushrooms, spinach, asparagus, cauliflower.
Some medicines are also believed to make gout more likely. These include:
• certain diuretics (“water pills”)
• niacin (a B-complex vitamin)
• aspirin (taken in low doses)
• cyclosporine (brand names: Sandimmune, Neoral, SangCya)
• some drugs used to treat cancer
Treatment
Treatment is generally performed by your GP via medications and diet control. If you don’t get treatment, a gout attack can last for days or even weeks. If you keep having more attacks, more joints will be affected, and the attacks will last longer.
If you have gout attacks for many years, you may develop soft tissue swellings of uric acid crystals called tophi in your joints. Tophi usually form on the toes, fingers, hands and elbows. You may also get kidney disease or kidney stones. Over time, the bone around a joint may be destroyed by gout causing arthritis in that joint.
To help prevent gout, your doctor may prescribe medicines to prevent future gout attacks. These medicines can help wash the uric acid from your joints, reduce swelling and keep uric acid from forming.
If you are overweight, it is helpful to lose the weight, even half a kilogram will help your joints. If you have high blood pressure or high cholesterol, get treatment and follow a low-salt, low-fat diet. Stay away from alcohol and foods that are high in purines and drink plenty of water to help flush the uric acid from your body.


